Do you hate errors in production ? If yes use typescript for type-safety development.
TypeScript is an open-source strongly typed programming language built over JavaScript.
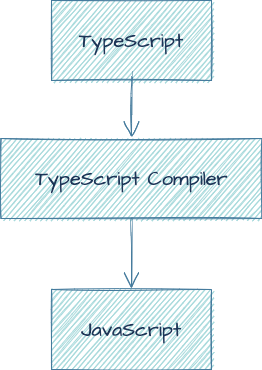
With typescript, we define a type for variables and functions, after that by using a typescript compiler, we compile typescript code to javascript code. We use typescript for development, but for production, javascript is the latest output.
Installation
Since we will use the NODEJS environment, firstly, you need to install NODEJS and NPM.
Install the typescript compiler
npm install -g typescript ts-nodeTo check the installation, you can run
tsc -vIf you are seeing a version of typescript it means, it installed successfully.

Types
String
For texts, we use the “string” type. Just like javascript, typescript also uses double quotes (“) or single quotes (‘) or backquote (`) characters to surround string data.
let language: string = "Javascript";
let language: string = "";
let language: string = "Javascript";Number
Number type is valid for integers, float numbers.
let sum: number = 0;
let sum: number = -5;
let sum: number = 0.7;For big integers, you can use the “bigint” type.
let big: bigint = 100n;Boolean
One of the most known type is boolean. To define true/false status, boolean is useful.
let isApproved: boolean = false;
let isApproved: boolean = true;Symbol
let sym1: Symbol = Symbol();
let sym2: Symbol = Symbol("key");Functions
function add(a:number, b:number) : number {
return a + b;
}
function (a:number, b:number) : number {
return a + b;
}
const add = (firstName: string, lastName: string) : string => {
return firstName + ' ' + lastName;
}if you don’t return anything you need use the void type.
const logger = (a: number): void => {
console.log(a);
};Object Destruction
Object destruction is one of the popular features of modern Javascript. Using typescript is also possible with object destruction.
const { foo }: { foo: string } = bar;Array Destruction
Same as object destruction, you can use typescript for array destruction easily.
function f([a, b, c]: [number, string, number]) {}Array
We use arrays for storing a list of elements. There are two ways to define a type for an array.
let nums: number[] = [1, 2, 3, 3];
let multi: number[][] = [
[1, 2, 3],
[23, 24, 25],
];
// or
let list: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3];Class
If you need to return an instance of class, you can use class as a type.
class A {}
function create(ctor: { new (): A }): A {
return new ctor();
}
let a = create(A);Any
Any means, it might be any type. If you use any, then you don’t need to use typescript, because any type will skip all typescript checks.
let result: any;
let getUser = (id: number): any => {
return this.db.getUser(id);
};Interface
To create a new type you can use interfaces. In the below example, I defined the User Interface. According to the definition, the user type includes id and name attributes.
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
const user = res.data as User;
console.log(user.name);Using Multiple Types
You can assign multiple types to variables. Let’s look at the below example, we have a function to find the user record in the database. If the id parameter is exists in the database, it returns the User. If not, it will return null. In this case, we have 2 different return types “User” and “null”. So, you can use multiple types for this type of case.
let getUser = (id: number): User | null => {
return this.db.getUser(id);
};Advanced Types and Utilities
Typescript offers powerful type utilities like Partial<T>, Readonly<T>, and Record<K, T>, which allow for more flexible and safe type transformations. For example:
type PartialUser = Partial<User>;
type ReadonlyUser = Readonly<User>;Generics
Generics enhance code reusability and type safety. They allow you to create components that work with any type:
function identity<T>(arg: T): T {
return arg;
}
let output = identity<string>("myString");Decorators
TypeScript decorators provide a way to add annotations and a meta-programming syntax for class declarations and members. Decorators can be used to modify class properties, methods, and accessors.
function sealed(constructor: Function) {
Object.seal(constructor);
Object.seal(constructor.prototype);
}
@sealed
class Greeter {...}`Advanced Type Manipulation
Type manipulation features like Mapped Types, Conditional Types, and Utility Types allow for more dynamic and flexible code structures.
type Keys = 'option1' | 'option2';
type Flags = { [K in Keys]: boolean };`Final
If you are familiar with any statically typed language(java, c, etc.), learning typescript is really easy. And typescript helps us catch errors on development by assigning types to variables. For less bug on production, use typescript.